DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of periodontal disease starts with taking the patient’s medical history to discover any past or current periodontal issues, as well as the presence of other diseases and medications which could play a role in the problem. A general assessment of patient’s oral hygiene and home dental care practices are also included in this first phase of the diagnosis.
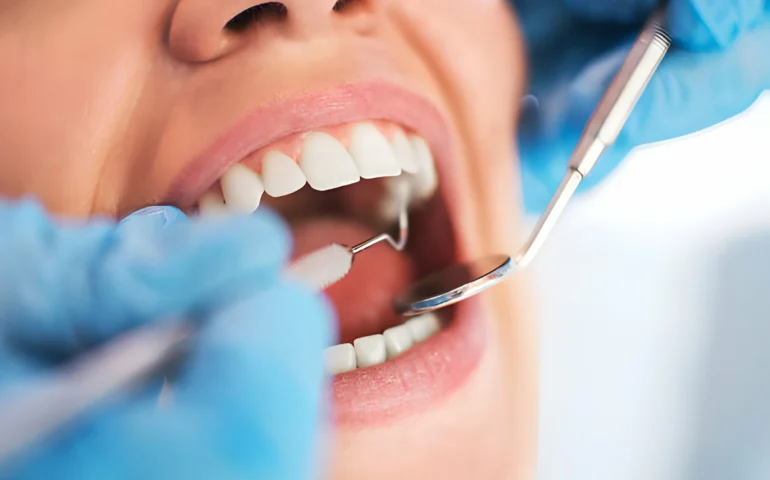
The next phase of the diagnosis focuses on an inspection of the gums. This inspection includes an examination of the color and shape of the gums on either side of each tooth. Inflammation, which is usually indicated by redness and/or bleeding upon the area being probed, can be the first hint that periodontal disease could be present. Another indication of the presence of periodontal disease can be found in the formation of the gums between teeth. If this area is blunt or flat as opposed to pointed, a more severe state of the disease may be present.
Diagnosis then moves on to testing for the movement or looseness of a patient’s teeth. Loose teeth can indicate that disease is present at deeper levels and that bone support is weakening. X-rays are then taken to confirm or refute the loss of the bone structure which supports the teeth. This process requires eighteen x-rays to make up the full mouth series necessary for a complete diagnosis.
If periodontal disease is determined to be present the next phase is treatment. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, you could be at the early stages of periodontal disease. For a full diagnosis and an early start on fighting this disease, call us today.




